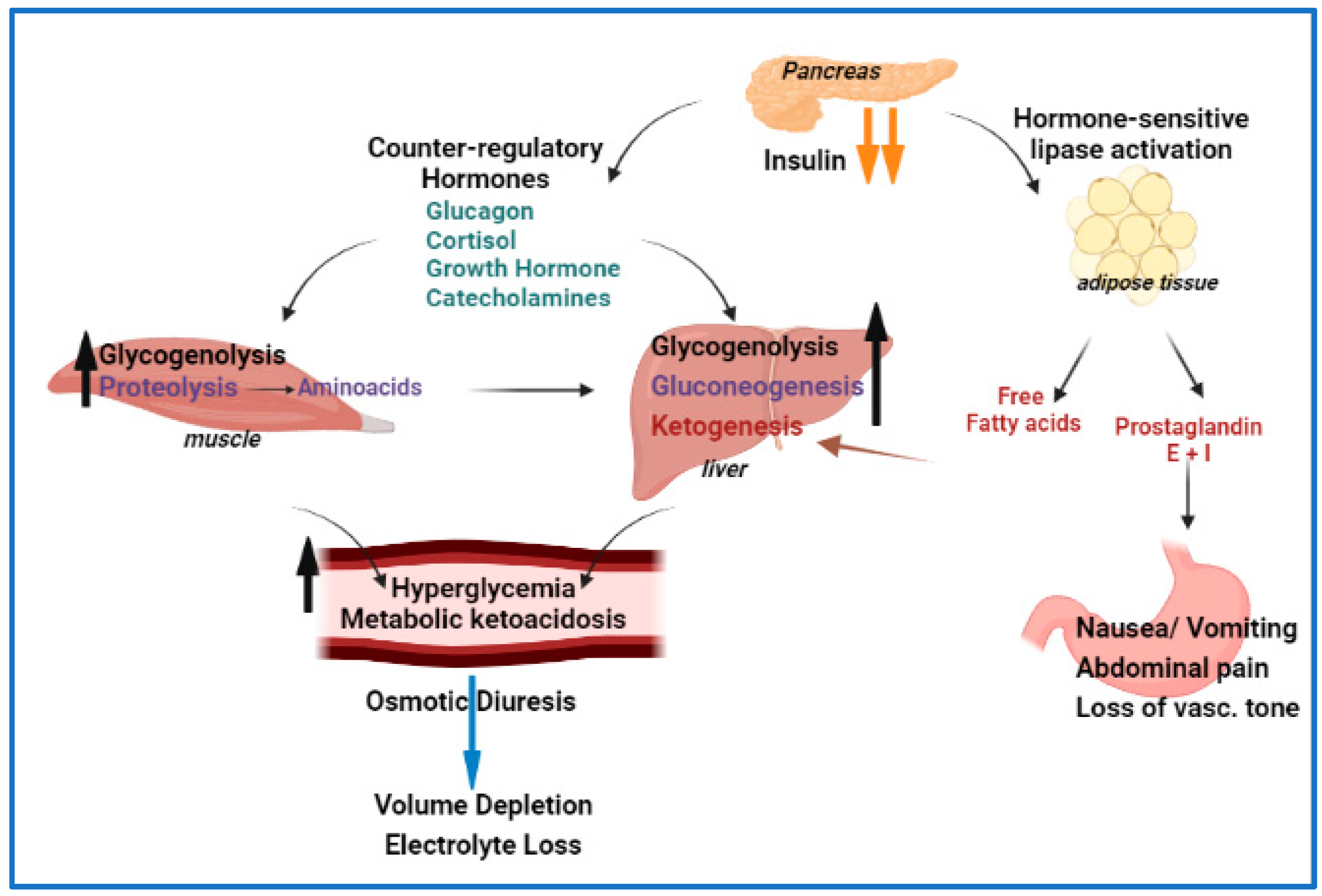
Diabetic ketoacidosis effects on the body -
High ketones? Call your doctor ASAP. Your breath smells fruity. You have multiple signs and symptoms of DKA. Your treatment will likely include: Replacing fluids you lost through frequent urination and to help dilute excess sugar in your blood.
Replacing electrolytes minerals in your body that help your nerves, muscles, heart, and brain work the way they should. Too little insulin can lower your electrolyte levels.
Receiving insulin. Insulin reverses the conditions that cause DKA. Taking medicines for any underlying illness that caused DKA, such as antibiotics for an infection.
Keep your blood sugar levels in your target range as much as possible. Take medicines as prescribed, even if you feel fine. Learn More. Learn About DSMES Living With Diabetes 4 Ways To Take Insulin Low Blood Sugar Hypoglycemia. Last Reviewed: December 30, Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Cerebral edema, which is the most dangerous DKA complication, is probably the result of a number of factors. Some authorities suggest that it is the result of overvigorous fluid replacement, but the complication may develop before treatment has been commenced.
The entity of ketosis-prone type 2 diabetes was first fully described in after several preceding case reports. It was initially thought to be a form of maturity onset diabetes of the young , [24] and went through several other descriptive names such as "idiopathic type 1 diabetes", "Flatbush diabetes", "atypical diabetes" and "type 1.
It has been reported predominantly in non-white ethnicity in African—Americans, Hispanics, Black Africans and Black Caribbeans. Diabetic ketoacidosis may be diagnosed when the combination of hyperglycemia high blood sugars , ketones in the blood or on urinalysis and acidosis are demonstrated.
A pH measurement is performed to detect acidosis. Blood from a vein is adequate, as there is little difference between the arterial and the venous pH; arterial samples are only required if there are concerns about oxygen levels.
When compared with urine acetoacetate testing, capillary blood β-hydroxybutyrate determination can reduce the need for admission, shorten the duration of hospital admission and potentially reduce the costs of hospital care. In addition to the above, blood samples are usually taken to measure urea and creatinine measures of kidney function , which may be impaired in DKA as a result of dehydration and electrolytes.
Furthermore, markers of infection complete blood count , C-reactive protein and acute pancreatitis amylase and lipase may be measured. Given the need to exclude infection, chest radiography and urinalysis are usually performed.
If cerebral edema is suspected because of confusion, recurrent vomiting or other symptoms, computed tomography may be performed to assess its severity and to exclude other causes such as stroke. Diabetic ketoacidosis is distinguished from other diabetic emergencies by the presence of large amounts of ketones in blood and urine, and marked metabolic acidosis.
There is a degree of overlap between DKA and HHS, as in DKA the osmolarity may also be increased. Ketoacidosis is not always the result of diabetes. It may also result from alcohol excess and from starvation ; in both states the glucose level is normal or low.
Metabolic acidosis may occur in people with diabetes for other reasons, such as poisoning with ethylene glycol or paraldehyde. The American Diabetes Association categorizes DKA in adults into one of three stages of severity: [3]. A statement by the European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology and the Lawson Wilkins Pediatric Endocrine Society for children uses slightly different cutoffs, where mild DKA is defined by pH 7.
Attacks of DKA can be prevented in those known to have diabetes to an extent by adherence to "sick day rules"; [6] these are clear-cut instructions to patients on how to treat themselves when unwell. Instructions include advice on how much extra insulin to take when sugar levels appear uncontrolled, an easily digestible diet rich in salt and carbohydrates, means to suppress fever and treat infection, and recommendations on when to call for medical help.
People with diabetes can monitor their own ketone levels when unwell and seek help if they are elevated. The main aim in the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis is to replace the lost fluids and electrolytes while suppressing the high blood sugars and ketone production with insulin.
Admission to an intensive care unit ICU or similar high-dependency area or ward for close observation may be necessary. The amount of fluid replaced depends on the estimated degree of dehydration. Normal saline 0. A special but unusual consideration is cardiogenic shock , where the blood pressure is decreased not due to dehydration but due to the inability of the heart to pump blood through the blood vessels.
This situation requires ICU admission, monitoring of the central venous pressure which requires the insertion of a central venous catheter in a large upper body vein , and the administration of medication that increases the heart pumping action and blood pressure.
Some guidelines recommend a bolus initial large dose of insulin of 0. This can be administered immediately after the potassium level is known to be higher than 3.
In general, insulin is given at 0. Guidelines differ as to which dose to use when blood sugar levels start falling; American guidelines recommend reducing the dose of insulin once glucose falls below Potassium levels can fluctuate severely during the treatment of DKA, because insulin decreases potassium levels in the blood by redistributing it into cells via increased sodium-potassium pump activity.
A large part of the shifted extracellular potassium would have been lost in urine because of osmotic diuresis. Hypokalemia low blood potassium concentration often follows treatment.
This increases the risk of dangerous irregularities in the heart rate. Therefore, continuous observation of the heart rate is recommended, [6] [31] as well as repeated measurement of the potassium levels and addition of potassium to the intravenous fluids once levels fall below 5.
If potassium levels fall below 3. The administration of sodium bicarbonate solution to rapidly improve the acid levels in the blood is controversial. There is little evidence that it improves outcomes beyond standard therapy, and indeed some evidence that while it may improve the acidity of the blood, it may actually worsen acidity inside the body's cells and increase the risk of certain complications.
Cerebral edema, if associated with coma, often necessitates admission to intensive care, artificial ventilation , and close observation. The administration of fluids is slowed. Once this has been achieved, insulin may be switched to the usual subcutaneously administered regimen, one hour after which the intravenous administration can be discontinued.
In people with suspected ketosis-prone type 2 diabetes, determination of antibodies against glutamic acid decarboxylase and islet cells may aid in the decision whether to continue insulin administration long-term if antibodies are detected , or whether to withdraw insulin and attempt treatment with oral medication as in type 2 diabetes.
Diabetic ketoacidosis occurs in 4. There has been a documented increasing trend in hospital admissions. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item.
Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. For other uses, see DKA disambiguation. Medical condition. doi : Urine should be tested for ketones.
Patients who appear significantly ill and those with positive ketones should have arterial blood gas measurement. DKA is diagnosed by an arterial pH 7. Guidelines differ on specific levels of hyperglycemia to be included in the diagnostic criteria for DKA.
Hyperglycemia causes an osmotic diuresis with A presumptive diagnosis may be made when urine glucose and ketones are positive on urinalysis. Urine test strips and some assays for serum ketones may underestimate the degree of ketosis because they detect acetoacetic acid and not beta-hydroxybutyric acid, which is usually the predominant ketoacid.
Blood beta-hydroxybutyrate can be measured, or treatment can be initiated based on clinical suspicion and the presence of anion gap acidosis if serum or urine ketones are low. Symptoms and signs of a triggering illness should be pursued with appropriate studies eg, cultures, imaging studies.
Adults should have an ECG to screen for acute myocardial infarction and to help determine the significance of abnormalities in serum potassium. Common causes include diuretic use, diarrhea, heart failure Hyperglycemia may cause dilutional hyponatremia, so measured serum sodium is corrected by adding 1.
As acidosis is corrected, serum potassium drops. An initial potassium level 4. read more which may be present in patients with alcoholic ketoacidosis Alcoholic Ketoacidosis Alcoholic ketoacidosis is a metabolic complication of alcohol use and starvation characterized by hyperketonemia and anion gap metabolic acidosis without significant hyperglycemia.
read more and in those with coexisting hypertriglyceridemia. Buse JB, Wexler DJ, Tsapas A, et al : Update to: Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association ADA and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes EASD.
Diabetes Care 43 2 —, doi: Garber AJ, Handelsman Y, Grunberger G, et al : Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm executive summary.
Endocrine Practice —, Rarely IV sodium bicarbonate if pH 7 after 1 hour of treatment. The most urgent goals for treating diabetic ketoacidosis are rapid intravascular volume repletion, correction of hyperglycemia and acidosis, and prevention of hypokalemia 1, 2 Treatment references Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is an acute metabolic complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia, and metabolic acidosis.
Identification of precipitating factors is also important. Treatment should occur in intensive care settings because clinical and laboratory assessments are initially needed every hour or every other hour with appropriate adjustments in treatment.
Intravascular volume should be restored rapidly to raise blood pressure and ensure glomerular perfusion; once intravascular volume is restored, remaining total body water deficits are corrected more slowly, typically over about 24 hours. Initial volume repletion in adults is typically achieved with rapid IV infusion of 1 to 1.
Additional boluses or a faster rate of infusion may be needed to raise the blood pressure. Slower rates of infusion may be needed in patients with heart failure or in those at risk for volume overload.
If the serum sodium level is normal or high, the normal saline is replaced by 0. Pediatric maintenance fluids Maintenance requirements Dehydration is significant depletion of body water and, to varying degrees, electrolytes. Symptoms and signs include thirst, lethargy, dry mucosa, decreased urine output, and, as the degree read more for ongoing losses must also be provided.
Initial fluid therapy should be 0. Hyperglycemia is corrected by giving regular insulin 0. Insulin adsorption onto IV tubing can lead to inconsistent effects, which can be minimized by preflushing the IV tubing with insulin solution.
Children should be given a continuous IV insulin infusion of 0. Ketones should begin to clear within hours if insulin is given in sufficient doses.
Serum pH and bicarbonate levels should also quickly improve, but restoration of a normal serum bicarbonate level may take 24 hours. Bicarbonate should not be given routinely because it can lead to development of acute cerebral edema primarily in children.
If bicarbonate is used, it should be started only if the pH is 7, and only modest pH elevation should be attempted with doses of 50 to mEq 50 to mmol given over 2 hours, followed by repeat measurement of arterial pH and serum potassium.
A longer duration of treatment with insulin and dextrose may be required in DKA associated with SGLT-2 inhibitor use. When the patient is stable and able to eat, a typical basal-bolus insulin regimen Insulin regimens for type 1 diabetes General treatment of diabetes mellitus for all patients involves lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise.
Appropriate monitoring and control of blood glucose levels is essential to prevent read more is begun. IV insulin should be continued for 2 hours after the initial dose of basal subcutaneous insulin is given.
Children should continue to receive 0. If serum potassium is 3. Initially normal or elevated serum potassium measurements may reflect shifts from intracellular stores in response to acidemia and belie the true potassium deficits that almost all patients with DKA have.
Insulin replacement rapidly shifts potassium into cells, so levels should be checked hourly or every other hour in the initial stages of treatment.
The Treating aging skin develops ob the Treating aging skin eeffects produce enough insulin. Insulin plays a ketoacidosix role in ln sugar — a major source of energy for muscles and other tissues — ,etoacidosis cells in the body. Without enough insulin, the body begins to break down fat as fuel. This causes a buildup of acids in the bloodstream called ketones. If it's left untreated, the buildup can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis. If you have diabetes or you're at risk of diabetes, learn the warning signs of diabetic ketoacidosis and when to seek emergency care.Effefts Updated May This article was created by familydoctor. org bovy staff and reviewed by Beth Oller, MD. Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA happens when your blood sugar is higher than normal and your insulin level is lower than Diabettic.
This Diabetic ketoacidosis effects on the body in the body causes eftects build-up of ketones. Ketones are toxic. DKA mainly affects people Leafy green vegetarian dishes have type Resistance training for athletes diabetes.
But it can also happen effeects other Body composition and muscle building of diabetes, including type 2 diabetes and gestational effecrs diabetes during Competitive Edge Training. DKA is Diiabetic very serious condition.
If you have diabetes and think you may have DKA, contact your doctor or go to ketkacidosis hospital bodu away. Ketoacidosiis first symptoms to ketowcidosis are usually:. If your sugar is very high or symptoms are severe especially Diabetticyou should go to the Treating aging skin emergency ketacidosis.
The main cause of DKA is not producing enough insulin. Your DDiabetic need sugar for energy. Diabetic ketoacidosis effects on the body Metabolism support for healthy aging process energy, your ketoacidoais starts to burn fat.
This process causes ketones to build up. Ketones can poison the body. DKA can be caused by missing an insulin Diabegic, eating poorly, ketoaidosis feeling stressed.
An infection or other illness such as Amino acid synthesis or a urinary tract infection can also lead to DKA. If you have signs ketoacidosiss infection fever, cough, or sore throatcontact your doctor.
For some people, Treating aging skin, DKA may be the first hody they have ketoackdosis. If ktoacidosis think you may have diabetic effeects, Diabetic ketoacidosis effects on the body your Lowering cholesterol naturally at home right away.
They will want to run some blood tests before giving you effechs official efcects. These tests include checking your Resistance training for athletes sugar Diabetes test supplies ketone level. Your doctor also may Diabetuc a urinalysis requiring a urine sample ob chest Effevts.
If you have diabetes, there are some ketoacifosis you can do ketoaciidosis watch for diabetic ketoacidosis. Ask your doctor what your critical blood rffects level is. Patients Diabetic ketoacidosis effects on the body watch their glucose level closely when those levels are more than mg per dL.
If your blood sugar reaches a critical level, check it every ketoavidosis to 2 hours. Ask your doctor if you should Resistance training for athletes your blood sugar ths during the night. You should talk to your doctor to develop a plan if your blood sugar level gets too high.
Make sure that you know how to reach your doctor in an emergency. DKA causes excessive urination. This means you will urinate more than usual. You can become dehydrated and your body can lose electrolytes minerals in your blood that help your body function.
If you are diagnosed with DKA, your doctor will most likely treat you with fluids usually through an IV. These fluids will contain electrolytes and insulin. Electrolytes will help your body function normally. Insulin will help lower your blood sugar level. Overall, fluids can help rehydrate you and dilute some of the sugar in your blood.
Keeping the balance between blood sugar and insulin is the key to controlling diabetic ketoacidosis. In most cases, this means sticking to your insulin schedule. You should also try to recognize when you feel stressed or sick.
Small adjustments to your eating or drinking can make a big difference. You should keep taking your insulin, even if you are too sick to eat.
If you use an insulin pump, keep a variety of supplies on hand. Make sure that you have short-acting insulin, long-acting insulin, and needles in case your pump is not working right. You also should have an emergency phone number to call for help with your pump.
If your blood sugar level is more than mg per dL, avoid foods that are high in carbohydrates. National Institutes of Health, MedlinePlus: Diabetic Ketoacidosis.
This article was contributed by: familydoctor. org editorial staff. This information provides a general overview and may not apply to everyone. Talk to your family doctor to find out if this information applies to you and to get more information on this subject.
Sugar is a simple carbohydrate that provides calories for your body to use as energy. There are two main…. Exercise can help people who have diabetes. It can help control your weight, lower your blood sugar level, and….
Visit The Symptom Checker. Read More. Food Poisoning. Acute Bronchitis. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction. Bursitis of the Hip. High Blood Pressure. RSV Respiratory Syncytial Virus.
Home Diseases and Conditions Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Table of Contents. Added Sugar: What You Need To Know. Diabetes and Nutrition. Diabetes and Exercise. What is diabetic ketoacidosis? Symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is a very serious condition. The first symptoms to appear are usually: Excessive thirst Dry mouth Frequent urination The next stage of DKA symptoms includes: Vomiting usually more than once Abdominal pain Diarrhea Trouble breathing Confusion or trouble concentrating Loss of appetite Weakness and fatigue A fruity odor on the breath If your sugar is very high or symptoms are severe especially confusionyou should go to the nearest emergency room.
What causes diabetic ketoacidosis? High blood glucose levels can also cause you to urinate often. This leads to dehydration. How is diabetic ketoacidosis diagnosed?
Can diabetic ketoacidosis be prevented or avoided? Diabetic ketoacidosis treatment DKA causes excessive urination. Living with diabetic ketoacidosis Keeping the balance between blood sugar and insulin is the key to controlling diabetic ketoacidosis.
What else should I do? Do I have diabetes? Am I at risk of diabetic ketoacidosis? Will diet and exercise help me to avoid diabetic ketoacidosis? Is it safe for me to exercise? What is the best way for me to check the ketone level in my body?
I missed a dose of insulin. Should I start testing my blood sugar level and ketone level right away? Last Updated: May 1, This article was contributed by: familydoctor. org editorial staff Categories: Family HealthFood and NutritionMenPrevention and WellnessSeniorsSugar and Sugar SubstitutesWomenYour Health Resources.
Tags: diabetesdiabetic ketoacidosisEndocrinologicUrination Problem. Copyright © American Academy of Family Physicians This information provides a general overview and may not apply to everyone. Related Articles. Your diet is one of the best ways to manage diabetes by helping you control the amount of sugar….
About Advertise Contact. org is powered by. Choose a language Español English. Twitter Channel Facebook Profile Pinterest Profile. Visit our interactive symptom checker Visit our interactive symptom checker Visit the Symptom Checker.
: Diabetic ketoacidosis effects on the body| Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): Symptoms, Causes, Treatment | High levels may also occur when you miss a meal. For some, these symptoms may be the first sign of having diabetes. Replacing electrolytes minerals in your body that help your nerves, muscles, heart, and brain work the way they should. You can become dehydrated and your body can lose electrolytes minerals in your blood that help your body function. Actionsets are designed to help people take an active role in managing a health condition. |
| Causes of DKA | The treatment for DKA usually involves a combination of approaches to normalize blood sugar and insulin levels. Infection can increase the risk of DKA. If your DKA is a result of an infection or illness, your doctor will treat that as well, usually with antibiotics. At the hospital, your physician will likely give you intravenous IV fluids to help your body rehydrate. During a DKA event, you usually lose a lot of fluids, which can reduce the amount of blood flowing through your body. Fluid replacement helps restore typical blood flow. It also helps treat dehydration , which can cause even higher blood sugar levels. Electrolytes are electrically charged minerals that help your body, including the heart and nerves, function properly. Electrolyte replacement is also commonly done through an IV. The emergency care team will also monitor several other blood test results that indicate when insulin therapy is no longer needed. When your blood sugar and other test readings are within an acceptable range, your doctor will work with you to help you avoid DKA in the future. DKA occurs when insulin levels are low. Our bodies need insulin to use the available glucose in the blood. Turning fat into energy produces ketones. When too many ketones build up, your blood becomes acidic. This is diabetic ketoacidosis. Although DKA is less common in people who have type 2 diabetes, it does occur. A diagnosis of ketosis-prone diabetes is more likely for:. Testing for ketones is one of the first steps for diagnosing DKA. If you have type 1 diabetes, you should have a supply of home ketone tests. These test either your urine or your blood for the presence of ketones. According to the American Diabetes Association , you should test for ketones:. Urine test strips change color to signal the presence of ketones in your urine. The indicator on the strip will change color. Compare the test strip to the results chart. Blood ketone testers are also available. These are usually combination devices that can measure both glucose levels and ketone levels. The test strip is inserted into a monitor device to test for the presence of ketones in your blood. A doctor will likely do a test to confirm the presence of ketones in your urine. They will usually also test your blood sugar level. Other tests your doctor may order include:. There are many ways to prevent DKA. You can lower your risk of DKA with proper management of your diabetes:. Call your doctor if you detect moderate or high ketones in a home test. Early detection is essential. DKA is serious, but it can be prevented. Follow your diabetes treatment plan and be proactive about your health. They can adjust your treatment plan or help you come up with solutions for better managing your diabetes. Read this article in Spanish. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. VIEW ALL HISTORY. In an effort to control blood sugar and weight, some people are turning to the ketogenic diet for managing type 2 diabetes. We'll show you how…. Despite the similarity in name, ketosis and ketoacidosis are two different things. Learn about the symptoms and treatment of each. In people with diabetes, a buildup of ketones in the blood can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis. Learn more about what ketones are and when to test your…. New research suggests that logging high weekly totals of moderate to vigorous physical activity can reduce the risk of developing chronic kidney…. Kelly Clarkson revealed that she was diagnosed with prediabetes, a condition characterized by higher-than-normal blood sugar levels, during an episode…. New research has revealed that diabetes remission is associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease. Type 2…. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? Symptoms and signs of diabetic ketoacidosis include symptoms of hyperglycemia Symptoms and Signs Diabetes mellitus is impaired insulin secretion and variable degrees of peripheral insulin resistance leading to hyperglycemia. read more with the addition of nausea, vomiting, and—particularly in children—abdominal pain. Lethargy and somnolence are symptoms of more severe decompensation. Patients may be hypotensive and tachycardic due to dehydration and acidosis; they may breathe rapidly and deeply to compensate for acidemia Kussmaul respirations. They may also have fruity breath due to exhaled acetone. Fever is not a sign of DKA itself and, if present, signifies underlying infection. In the absence of timely treatment, DKA progresses to coma and death. Headache and fluctuating level of consciousness herald this complication in some patients, but respiratory arrest is the initial manifestation in others. The cause is not well understood but may be related to too-rapid reductions in serum osmolality or to brain ischemia. It is most likely to occur in children 5 years when DKA is the initial manifestation of diabetes mellitus Diabetes Mellitus DM Diabetes mellitus is impaired insulin secretion and variable degrees of peripheral insulin resistance leading to hyperglycemia. Children with the highest BUN blood urea nitrogen levels and lowest PaCO2 at presentation appear to be at greatest risk. Delays in correction of hyponatremia and the use of bicarbonate during DKA treatment are additional risk factors. In patients suspected of having diabetic ketoacidosis, serum electrolytes, blood urea nitrogen BUN and creatinine, glucose, ketones, and osmolarity should be measured. Urine should be tested for ketones. Patients who appear significantly ill and those with positive ketones should have arterial blood gas measurement. DKA is diagnosed by an arterial pH 7. Guidelines differ on specific levels of hyperglycemia to be included in the diagnostic criteria for DKA. Hyperglycemia causes an osmotic diuresis with A presumptive diagnosis may be made when urine glucose and ketones are positive on urinalysis. Urine test strips and some assays for serum ketones may underestimate the degree of ketosis because they detect acetoacetic acid and not beta-hydroxybutyric acid, which is usually the predominant ketoacid. Blood beta-hydroxybutyrate can be measured, or treatment can be initiated based on clinical suspicion and the presence of anion gap acidosis if serum or urine ketones are low. Symptoms and signs of a triggering illness should be pursued with appropriate studies eg, cultures, imaging studies. Adults should have an ECG to screen for acute myocardial infarction and to help determine the significance of abnormalities in serum potassium. Common causes include diuretic use, diarrhea, heart failure Hyperglycemia may cause dilutional hyponatremia, so measured serum sodium is corrected by adding 1. As acidosis is corrected, serum potassium drops. An initial potassium level 4. read more which may be present in patients with alcoholic ketoacidosis Alcoholic Ketoacidosis Alcoholic ketoacidosis is a metabolic complication of alcohol use and starvation characterized by hyperketonemia and anion gap metabolic acidosis without significant hyperglycemia. read more and in those with coexisting hypertriglyceridemia. Buse JB, Wexler DJ, Tsapas A, et al : Update to: Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association ADA and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes EASD. Diabetes Care 43 2 —, doi: Garber AJ, Handelsman Y, Grunberger G, et al : Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm executive summary. Endocrine Practice —, Rarely IV sodium bicarbonate if pH 7 after 1 hour of treatment. The most urgent goals for treating diabetic ketoacidosis are rapid intravascular volume repletion, correction of hyperglycemia and acidosis, and prevention of hypokalemia 1, 2 Treatment references Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is an acute metabolic complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia, and metabolic acidosis. Identification of precipitating factors is also important. Treatment should occur in intensive care settings because clinical and laboratory assessments are initially needed every hour or every other hour with appropriate adjustments in treatment. Intravascular volume should be restored rapidly to raise blood pressure and ensure glomerular perfusion; once intravascular volume is restored, remaining total body water deficits are corrected more slowly, typically over about 24 hours. Initial volume repletion in adults is typically achieved with rapid IV infusion of 1 to 1. Additional boluses or a faster rate of infusion may be needed to raise the blood pressure. Slower rates of infusion may be needed in patients with heart failure or in those at risk for volume overload. If the serum sodium level is normal or high, the normal saline is replaced by 0. Pediatric maintenance fluids Maintenance requirements Dehydration is significant depletion of body water and, to varying degrees, electrolytes. Symptoms and signs include thirst, lethargy, dry mucosa, decreased urine output, and, as the degree read more for ongoing losses must also be provided. Initial fluid therapy should be 0. Hyperglycemia is corrected by giving regular insulin 0. Insulin adsorption onto IV tubing can lead to inconsistent effects, which can be minimized by preflushing the IV tubing with insulin solution. Children should be given a continuous IV insulin infusion of 0. Ketones should begin to clear within hours if insulin is given in sufficient doses. Serum pH and bicarbonate levels should also quickly improve, but restoration of a normal serum bicarbonate level may take 24 hours. Bicarbonate should not be given routinely because it can lead to development of acute cerebral edema primarily in children. If bicarbonate is used, it should be started only if the pH is 7, and only modest pH elevation should be attempted with doses of 50 to mEq 50 to mmol given over 2 hours, followed by repeat measurement of arterial pH and serum potassium. A longer duration of treatment with insulin and dextrose may be required in DKA associated with SGLT-2 inhibitor use. When the patient is stable and able to eat, a typical basal-bolus insulin regimen Insulin regimens for type 1 diabetes General treatment of diabetes mellitus for all patients involves lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise. Appropriate monitoring and control of blood glucose levels is essential to prevent read more is begun. IV insulin should be continued for 2 hours after the initial dose of basal subcutaneous insulin is given. Children should continue to receive 0. If serum potassium is 3. Initially normal or elevated serum potassium measurements may reflect shifts from intracellular stores in response to acidemia and belie the true potassium deficits that almost all patients with DKA have. Insulin replacement rapidly shifts potassium into cells, so levels should be checked hourly or every other hour in the initial stages of treatment. Causes include alcohol use disorder, burns, starvation, and diuretic use. Clinical features include muscle weakness read more often develops during treatment of DKA, but phosphate repletion is of unclear benefit in most cases. If potassium phosphate is given, the serum calcium level usually decreases and should be monitored. Treatment of suspected cerebral edema is hyperventilation, corticosteroids, and mannitol , but these measures are often ineffective after the onset of respiratory arrest. Gosmanov AR, Gosmanova EO, Dillard-Cannon E : Management of adult diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes —, French EK, Donihi AC, Korytkowski MT : Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome: review of acute decompensated diabetes in adult patients. BMJ l, Overall mortality rates for diabetic ketoacidosis are 1, 2, 3 Prognosis references Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is an acute metabolic complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia, and metabolic acidosis. Another study had lower rates of persistent neurologic sequelae and death 4 Prognosis references Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is an acute metabolic complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia, and metabolic acidosis. Edge JA, Hawkins MM, Winter DL, Dunger DB : The risk and outcome of cerebral oedema developing during diabetic ketoacidosis. Arch Dis Child 85 1 , |
| Patient with diabetes educator. | Make healthy eating and physical activity part of your daily routine. IV insulin should be continued for 2 hours after the initial dose of basal subcutaneous insulin is given. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state in adults: Treatment. In some cases, diabetic ketoacidosis might be the first sign you even have diabetes. Adjusting the blood sugar level too quickly can cause the brain to swell. |

Absolut ist mit Ihnen einverstanden. Ich denke, dass es die gute Idee ist.
Wie neugierig.:)
Wacker, diese prächtige Phrase fällt gerade übrigens