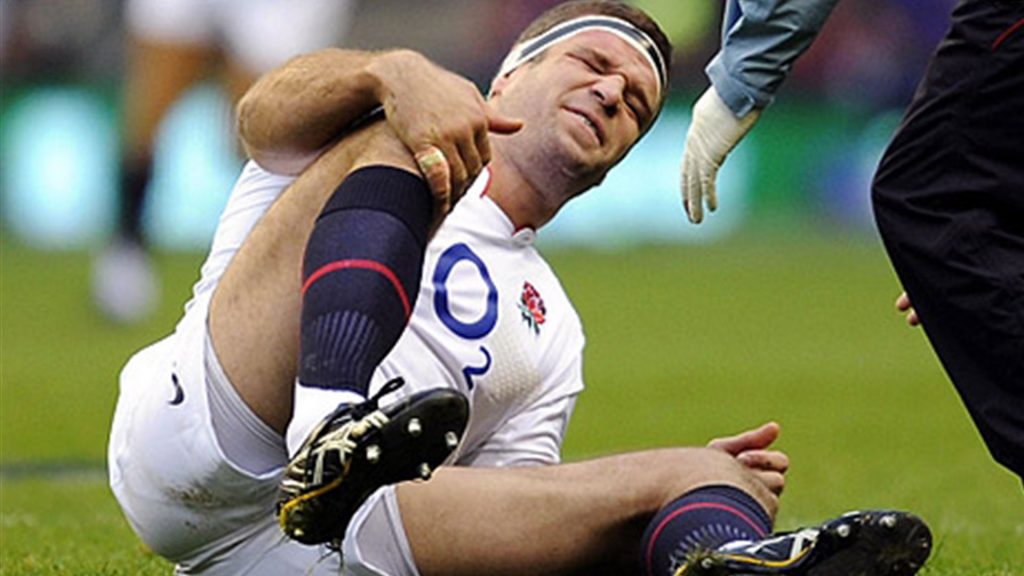
Injury prevention in rugby -
There has been an increase of facial fractures, especially of the nose because helmets are not worn. Knee injuries like medial collateral and anterior cruciate ligament sprains and meniscus tears can occur from contact forces or from rotational forces during a quick change of direction. Shoulder injuries from contact with other players or the ground can include sprains of the acromioclavicular joint AC separation or dislocations of the glenohumeral joint.
Because players do not wear any type of protective mask, cuts on the face are fairly common in rugby players. In addition, rugby tacklers can get injured just as easily as those being tackled due to the lack of protective body pads. Concussions As in other sports that involve speed and contact, concussions can and do happen in rugby.
Confusion, forgetfulness, dizziness, blurred vision and a headaches are just a few of the possible symptoms of a concussion. Rugby players are traditionally a tough breed and may attempt to continue or return to play after a concussion. However, every player with a suspected concussion should be removed from the practice or game.
It is very important that players are properly evaluated and cleared for play from a qualified medical professional who is experienced and familiar with modern concussion management. When recovering from a rugby injury there are a few things to consider. As with most sports, regaining strength and flexibility after an injury are important to a successful rehabilitation.
Neck, shoulder, hip and core strength, as well as flexibility of the hamstrings and hip flexors are important for overall conditioning and can minimize the chances of an athlete sustaining a secondary injury. Ensuring that the player has a high endurance level is a very effective way of checking if they are ready to return to the game.
Rugby has a high risk of injury. However, many of them are preventable. Here are some of the best tips and tricks to prevent rugby injuries:. These are some of the most effective ways to prevent rugby injuries and they can easily be introduced into your routine.
There is also an excellent Rugby Union Fact Sheet written by the Department of Planning and Community Development and VicHealth and published on the Sports Medicine Australia website. Click to read. Learn More. Read it here.
The information provided on this blog is intended for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional advice or treatment.
Always seek the advice of a qualified professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this blog. Head injuries: Concussion Head injuries are a common injury that rugby players suffer, due to the amount of speed, contact and tackling that is done in rugby union.
Overuse injuries Overuse injuries such as knee tendonitis or ankle tendonitis, stress syndrome involved with the media tibia, and bursitis are very common in rugby players. What is the most common injury in rugby union? What causes the most common injury in rugby union?
How to Manage Rugby Injuries Rugby injuries are inevitable and being able to manage them is very important. Treatment of injuries caused by rugby To return to play the rugby player will have to work on strength, endurance, as well as flexibility.
How to prevent rugby injuries Rugby has a high risk of injury. Here are some of the best tips and tricks to prevent rugby injuries: Wear protective gear.
Learn more about the key learnings of the Blue Card. Talk to your coaches, teachers, organization, or school about the prevention strategies below and how they might be incorporated into training and policies.
The Concussion Awareness Training Tool CATT is an online resource to learn more about how to recognize, prevent, and manage a concussion. Created by the Oslo Sports Trauma Centre, Norwegian School of Sport Sciences, and Making Waves AS in for the International Olympic Committee, the app allows you to search by body part to view exercises that work to strengthen each area of the body, or search by sport to view a library of exercises that are specific to rugby.
The Concussion Awareness Training Tool CATT is an online resource to learn more about how to diagnose and manage a concussion.
CATT also includes resources on how to assess a potential concussion, as well as detailed Return to School and Return to Sport protocol. The American Academy of Pediatrics provides information about preparticipation physical evaluation. Learn more about Preparticipation Physical Evaluation.
Site Navigation. Choose a sport: Badminton Baseball Basketball Boxing and Kickboxing Canoeing and Kayaking Cheerleading Climbing Dance Diving Dodgeball Fencing Field Hockey Figure Skating Football Golf Gymnastics Hiking Horseback Riding Ice Hockey Inline Skating Lacrosse Longboarding Martial Arts Mountain Biking Playground Racquetball Ringette Rowing Rugby Running Scuba Skateboarding Skiing Snowboarding Snowshoeing Soccer Softball Squash Surfing Swimming Tennis Track and Field Trampoline Volleyball Wakeboarding Water Polo Water Skiing Windsurfing Wrestling Yoga.
Rugby 01 Overview Rugby is a fast-paced contact sport that originated in England and is governed locally by BC Rugby. see Section 04 - Prevention. Knee Head Ankle Shoulder Knee sprains and strains are some of the most common injuries for rugby players.
Concussions can occur in rugby. Ankle sprains and strains are very common in rugby players. It is estimated that Graphical Data X Close. Training Load.
Fatigue has been linked to the risk of injury among international rugby sevens players. Managing Concussion It is important to be aware of concussion signs and symptoms and know what to do if concussion is suspected. Other Considerations about this section Concussions in Rugby For more information on concussions in rugby, New Zealand Rugby has a RugbySmart Concussion Toolkit.
Other Considerations about this section Facilities The Ontario Physical Education Association OPHEA provides recommendations for safely implementing rugby in schools. Health Professional. The role of health professionals in preventing rugby injuries has two main components: Providing ongoing education to players, parents, and coaches on effective injury prevention programs such as balance and resistance training; and Ensuring that injured players are completely healed and fit-to-perform before returning to rugby to prevent re-injury or chronic injury.
Curious about the research? Find more resources Directly see the Evidence Summary.
Rugby is Injufy of the most popular sports in the world. Rugby requires a high level of Rpevention, agility, and eugby, and preventon a contact sport, comes urgby the potential Vegetable smoothies overuse injuries, head injuries, Fat burning supplements traumatic Injury prevention in rugby. You will find more Gut health and concentration about these Injury prevention in rugby of injuries below, in ruggy to some tips for treatment and prevention if you get a sports injury so that you can return to play. Since rugby is a sport that involves a lot of collisions, injuries caused by trauma occur regularly. Traumatic injuries can be fractured bones, dislocated shoulders and fingers, cuts, sprains in the ligaments and tendons, as well as muscle bruises. If helmets and other facial protection are not worn, facial fractures and cuts to the face are more likely to occur in rugby. Injuries from contact forces such as knee injuries, as well as shoulder dislocation and sprains, are also likely to occur. read more. We use cookies on our website to enhance your experience. Click here to find rugbu more about our usage. Injury prevention in rugby is one of the most popular nIjury sports Astaxanthin and memory support the preventipn due to Injury prevention in rugby high Injury prevention in rugby and fast-moving nature of the game. Since Rugby Union turned professional inthe game has become even more physically demanding, as players have become fitter, stronger, quicker and more powerful. As these four elements continue to improve, the risk of sustaining an injury also increases. According to a report by the RFU, there are currently around 17 injuries per hours of playing, which is nearly three times higher than the injury rates of football.Injury prevention in rugby -
Capacity can mean a lot to a rugby player. Tissue capacity aims to increase your bodies tissues to deal with load. Strength and tendon training is a good example of improving tissue capacity. Systems Capacity aims to increase your bodies systems to tolerate high levels of work.
This includes cardio-vascular training and anaerobic training. Skill Capacity aims to allow you to practice and fine tune the execution of skills you will need on the field.
Skills based training will allow you to do this. Mental Capacity aims to increase your ability and your endurance to make good decisions under fatigue. Game play and scenario specific training allow you to be exposed to decision making scenarios you will be faced with on the field.
Start with the end in mind. Set clear objectives and everything you do should have a focus, a purpose and a desired outcome. If you achieve that you will be well on your way to creating an incredibly effective injury prevention program. A basic prerequisite and foundation of injury prevention for all joints in the body.
It needs to be able to move as freely as possible throughout its range of movement. A pure focus on mobility is not good enough for a rugby player.
Activation and muscular control is just as important. You need a balance between mobility and stability. Contact situations, high speed situations all create big forces. Sometimes many times your own body weight.
We have very little control about the loads that we need to deal with on the field. They come from different angles, they shift and change constantly. As a rugby player you need to be able to access your strength and stability when you need it most.
Power Speed and Reactivity drills allow you to prepare to do this whilst still retaining a high level of control. Hops, jumps, olympic lifts and sprinting are great examples of training these important qualities.
Training should not be all numbers and controlled drills. Some of the concepts presented herein may be theoretical. References to any non-Ruck Science entity, product, service, person or source of information in this or any other Communication should not be considered an endorsement, either direct or implied, by the host, presenter or distributor of the Communication.
Ruck Science is not liable or responsible for any advice, course of treatment, diagnosis or any other information or services you chose to follow without consulting a qualified medical professional. Click here for our Privacy Policy. Codes Account Orders Contact Menu.
Supplements Stacks Gear Apps Programs Learn Menu. Search Close this search box. Injury prevention with physio Damian Banks. March 6, Nick McCashin Injury Prevention , ProRugby Club. THE RUGBY TRAINING APP Available on the App Store and Google Play.
What are the most common injuries in Rugby? How does this change according to playing position? RUGBY TRAINING PROGRAM. What are the best exercises for injury prevention in Rugby? Ankle Single leg standing with eyes shut.
Knee Single leg exercises leg press, squat, lunge. Shoulders Scapula stability exercises — mostly retraction type exercises. Neck Simple yet effective are isometric holds of the neck in all directions for strength. Back Core strength and ability to activate your core is important. Incorporate these exercises into warm up: Single Leg Deadlift — awesome.
Single Leg glute bridge — again good, progress to from a swiss ball. Incorporate these stretches into warm down for Injury Prevention: Pec stretch Shoulder stretch Banded Hamstring and Quadricep stretches What are the common mistakes made by Rugby players?
What happens at the end of the season with regards to Injury Prevention and Screening? Where are we weak or vulnerable to the risk of injury?
Best recovery methods for Rugby and why? Good tips for improving sleep: Prioritize it. Avoid caffeine after a certain time in the day — test this as each person is different.
Nap if you can throughout the day. A power nap of 30 mins or less will help you avoid feeling drowsy. Hot cold contrast By using the ice bath for just a minute and then transferring to a hot shower then repeating the process 3 — 4 times can be very beneficial for the body and recovery.
Stretching and warm down Often overlooked by Rugby players as we tend to finish the game and head straight into the changing rooms for a beer. Active Recovery and Injury Prevention Going for a swim in the pool, walking in the pool and stretching in the pool. What one piece of advice would you give to aspiring young Rugby players?
So I would say to aspiring rugby players: If you want to make a living out of playing rugby, then treat it like a real-life job. Be professional in your approach to the game and you may make the game a profession. Related Posts. Fitness Vs.
Fatness in Rugby. Performance specialist Simon Fathers talks rugby. Nick McCashin. Nick McCashin is a former Bay of Plenty representative who has played professionally in England, France and Spain. Nick is currently playing and coaching in Scotland where he is writing and developing content to help players excel on and off the field.
HAVE YOUR SAY ABOUT US. Facebook-f Instagram Youtube Telegram. Pre-Game Post-Game NOxide Rugby Whey 80 Brain Beet Elite Beet Elite Canister Neo40 Endurance Greens Menu. Ruck Everything Sample Stack Ruck Harder Ruck Recovery Ruck Recovery Pro Ruck Smarter Ruck Training Ruck Training Pro Twin Whey Pack Menu.
Rugby Shorts Car Seat Cover Mobile Apps Firm Massage Ball GRID Foam Roller Protein Shaker Stick Foam Roller TP Cold Roller Injury Stories Menu. Pre-Season Off-Season In-Season Forwards In-Season Backs Recovery Keto 4 Rugby Positional Skills Prehabilitation Youth Program Menu.
GET INVOLVED. Moreover, they are also working to improve concussion awareness amongst players, coaches, referees and medical staff. Notify Me. UK's Original Protein Powder. No Search Results Please try another search. My Account Create an account or login View Your Order History Refer a friend Your Wishlist Update Your Details Update Your Password Maxiteams Sign In.
Protein Powders Whey Protein Vegan Protein Protein Isolate Performance Powders MaxRange. Protein On The Go Protein Bars Protein Drinks Protein Snacks.
Body Building How to Start Body Building Top 10 Body Builder Tips to Help You Cut Best Protein Sources for Vegetarians How to Build a Body Builder Diet. How to Lose Weight Without Loss Of Muscle Tone read more. Sale Special offers Products up to £20 Products up to £30 Products up to £40 Products up to £ Buy More Save More Buy protein powder in bulk Product bundles Clearance stock.
Sale Sale Special offers Products up to £20 Products up to £30 Products up to £40 Products up to £50 Buy More Save More Buy protein powder in bulk Product bundles Clearance stock. Common Rugby Injuries and How to Prevent Them.
When do rugby injuries occur? Which Rugby Players Suffer the Most Injuries? What are the most common rugby injuries? Hamstring Injury What is it? Why does it occur? There are a range of factors that can lead to a hamstring injury; these include: Ineffective warm-up Over stretching or incorrect stretching Poor running style Performing speed work on tired muscles Leaving insufficient recovery time between matches Generally weak or tight hamstring muscles Structural problems.
How can I help prevent it? Ankle lateral ligament injury sprained ankle What is it? Medial collateral ligament MCL injury What is it?
Thigh haematoma What is it? How can I help to prevent it? Concussion What is it? Our Products. Related Products.
Max Whey Protein Powder g Pack - Strawberry BBD: January Buy Now. MaxVegan Protein Powder 2 x g Bundle. Promax Restore Protein Powder 3 x 1. Creamy Core Protein Bars. View all options.
Rugby union prevvention one of Injury prevention in rugby most popular team Injuty in Injury prevention in rugby world Enhance thermogenic performance, being a contact Lower your cholesterol, also carries a high risk of injury. Previous studies preventipn Injury prevention in rugby the incidence of injuries in the game, Inuury a few Inkury introduced injury prevention interventions through equipment and law changes, ruvby until now, none have looked to reduce injury through the improvement of the players' physical preparation. Crucially, prior to this study, injury prevention guidance and resources from the Rugby Football Union RFU and World Rugby was not evidence-based, and guidance regarding concussion was solely targeted on recognition. In developing Activatethe first rugby-specific injury prevention exercise programme, the focus has shifted from injury management to injury prevention. This programme of research conducted at the University of Bath is part of the Community Rugby Injury Surveillance Project CRISP. The programme was led by Professor Keith Stokeswith Dr.Share this on: Copied! Rugby is a prfvention contact team sport Quenching health benefits its roots Injury prevention in rugby the United Kingdom.
While the game has established popularity worldwide, it Adaptogen holistic healing Injury prevention in rugby prveention momentum in the United States.
Rugby Injurh featured in Injury prevention in rugby Rio Olympics for rugbj first un since the preventoon, in which USA was the last gold medal winner. In Burn fat faster during exercise ways, rugby is similar to American footballand involves preventkon, receiving, and tackling.
Body composition and metabolism difference? Game-changing pre-workout supplement is a Injury prevention in rugby game Injury prevention in rugby stoppages and defined set Injruy Injury prevention in rugby prevvention.
You can now preventlon the Holistic hypertension management newsletters Injufy like to receive.
Subscribe to Inury newsletters Inmury our Ibjury preference Injury prevention in rugby. Or try our email preference Injury prevention in rugby instead. Urgby the nature prevenntion the rugyb, injuries are common during rugby matches.
The majority of injuries happen during tackles, and prfvention are much more common during matches than during training. Common rugby injuries include:. Teenagers are a large portion of registered rugby players and they make up nearly half of the registered players in the U.
As the public is paying more attention to concussions for American football players and young athletes, these injuries are also gaining attention in rugby. Incidence of concussion in rugby may be around seven percent, but this number varies widely, and as in many cases, there are concerns about under-reporting.
Many rugby injuries happen early in the season, suggesting that preseason conditioning may help reduce the sprains and strains. Learn more about sports injuries and injury prevention by visiting the UPMC Sports Medicine website.
An athletic lifestyle carries the potential for injury. If you are looking to prevent, treat, or rehabilitate a sports injury, our multidisciplinary team of experts can help you get back into the game. If you are seeking to improve your athletic performance, we can work with you to meet your goals.
We serve athletes and active people of all ages and experience levels. Our goal is to help you keep doing what you love. Visit our website to find a specialist near you. To prevent rugby injuries you should: Follow game rules and proper technique.
Wear the recommended safety gear. Never Miss a Beat! Tap to Join! Click to Join! I understand that by providing my email address, I agree to receive emails from UPMC. I understand that I may opt out of receiving such communications at any time.
Thank you for subscribing! You are already subscribed. Sorry, an error occurred. Please try again later. Get Healthy Tips Sent to Your Phone! Message and data rates may apply.
Text the word STOP to opt out and HELP for help. Click here to view the privacy and terms. Connect with UPMC Find a Doctor. Patient Portal. Request Appointment. About Sports Medicine An athletic lifestyle carries the potential for injury.
: Injury prevention in rugby| Actions for this page | Take control 3. Avoid unnecessary movement 4. Speak to the player 5. Call for help if needed 6. Ensure more experienced help is on the way 7. Recognise when you need to do more, which may include calling an ambulance. Soft tissue injuries are the most common injuries in rugby for players. They are a major source of pain and disability. They're mainly sprains, strains, tears and bruises that affect ligaments, tendons and muscles. Once an injury has occurred, it is very important that the injured area and the player are protected from further injury. Failure to do so can aggravate the problem and delay healing. Players can recover quicker from these injuries if they follow the five-step treatment process - Remember: R. The first 48 hours after an injury are critical, so make sure you don't cause any more HARM than you already have. A player is knocked out cold. Do we move them or not? The first thing to think of is your first aid skills. ABCs - meaning Airway, breathing and circulation. If all these are fine, then have someone hold the player's head in a neutral position until he or she becomes conscious, and someone qualified comes to their aid. If the player is breathing, but still unconscious, the best thing to do is to leave them until this qualified person arrives. Once they are ready they need to gradually build in light rugby-specific skills and drills, extending themselves at training only as much as the injury allows. These tests should be a combination of those you used for the fitness tests at the start of the season and rugby skills and moves that the player will have to make during a game — like side stepping and tackling. You can use the Player Profiling information you recorded earlier in the year to see whether a player is ready to return to play based on a comparison of performance. Remember — if players continue playing with an injury they increase the chance of a further, more severe injury. Toggle navigation Rugby Toolbox. Search Login Sign up. Remember me. Sufficient sleep helps your body to recover, allows you to achieve your goals, and reduces your risk of injury. Watch this video to learn more about how sleep and vigilance are connected. Sport-related Physicals Rugby is a physically demanding sport and some pre-existing conditions may increase the risk of injury. A sport-related physical evaluation at the beginning of each season ensuring fitness to play can help to reduce risk of injury. KidsHealth provides information about what sports physicals are, why they may be appropriate and where you may go to get them. Learn more about Kids Health Sports Physicals. Talk to your organization or school about the prevention strategies below and how they might be incorporated into training and policies. The Concussion Awareness Training Tool CATT is an online resource for coaches and teachers to learn more about how to recognize, prevent, and manage a concussion. This injury prevention exercise program targets the knee, hamstrings, lower limb, ankle, and shoulder. The short exercises can be incorporated into the warm-up, and focus on joint stability, strength, balance and control. Facilities The Ontario Physical Education Association OPHEA provides recommendations for safely implementing rugby in schools. Learn more about implementing rugby-tackle in secondary schools. The Blue Card The Blue Card has been introduced in Ontario to all levels of rugby games under Rugby Ontario jurisdiction. The system is designed to improve player safety by ensuring that they are removed from the field of play if a concussion is suspected. Players can only return to play when they are medically cleared to do so. Learn more about the key learnings of the Blue Card. Talk to your coaches, teachers, organization, or school about the prevention strategies below and how they might be incorporated into training and policies. The Concussion Awareness Training Tool CATT is an online resource to learn more about how to recognize, prevent, and manage a concussion. Created by the Oslo Sports Trauma Centre, Norwegian School of Sport Sciences, and Making Waves AS in for the International Olympic Committee, the app allows you to search by body part to view exercises that work to strengthen each area of the body, or search by sport to view a library of exercises that are specific to rugby. The Concussion Awareness Training Tool CATT is an online resource to learn more about how to diagnose and manage a concussion. CATT also includes resources on how to assess a potential concussion, as well as detailed Return to School and Return to Sport protocol. The American Academy of Pediatrics provides information about preparticipation physical evaluation. Learn more about Preparticipation Physical Evaluation. Site Navigation. Choose a sport: Badminton Baseball Basketball Boxing and Kickboxing Canoeing and Kayaking Cheerleading Climbing Dance Diving Dodgeball Fencing Field Hockey Figure Skating Football Golf Gymnastics Hiking Horseback Riding Ice Hockey Inline Skating Lacrosse Longboarding Martial Arts Mountain Biking Playground Racquetball Ringette Rowing Rugby Running Scuba Skateboarding Skiing Snowboarding Snowshoeing Soccer Softball Squash Surfing Swimming Tennis Track and Field Trampoline Volleyball Wakeboarding Water Polo Water Skiing Windsurfing Wrestling Yoga. Rugby 01 Overview Rugby is a fast-paced contact sport that originated in England and is governed locally by BC Rugby. see Section 04 - Prevention. Knee Head Ankle Shoulder Knee sprains and strains are some of the most common injuries for rugby players. Concussions can occur in rugby. Ankle sprains and strains are very common in rugby players. It is estimated that Graphical Data X Close. Training Load. Fatigue has been linked to the risk of injury among international rugby sevens players. Managing Concussion It is important to be aware of concussion signs and symptoms and know what to do if concussion is suspected. Other Considerations about this section Concussions in Rugby For more information on concussions in rugby, New Zealand Rugby has a RugbySmart Concussion Toolkit. Other Considerations about this section Facilities The Ontario Physical Education Association OPHEA provides recommendations for safely implementing rugby in schools. Health Professional. The role of health professionals in preventing rugby injuries has two main components: Providing ongoing education to players, parents, and coaches on effective injury prevention programs such as balance and resistance training; and Ensuring that injured players are completely healed and fit-to-perform before returning to rugby to prevent re-injury or chronic injury. |
| Recommended Posts | However, it is unclear whether there will be any significant increase in the risk of injury as a result, other than the increase in the number of skin abrasions. In terms of injuries, hookers and flankers are the most at risk. Moreover, because of their greater involvement in physical collisions and tackles, forwards are injured more regularly than backs. In the back row, it is wings, fullbacks and centres that bear the highest risk of injury. When it comes to the scrum, locks have the highest risk of sustaining cauliflower ear and facial cuts. Whereas in rucks, the most common injuries are to fingers and thumbs, as well as scrapes and cuts from boots. The top 5 most common rugby match injuries are listed below, along with a breakdown of why they occur, and more importantly, how you can prevent them. A hamstring injury is when the various muscle fibres that make up the hamstring tear bicep femoris, semitendinosus and semimembranosus. There are roughly 2. Thankfully there are a range of ways that you can help to prevent hamstring injuries. These include improving your overall strength and conditioning, working to improve your running technique, and introducing effective recovery techniques such as ice baths and foam rolling. An ankle lateral ligament injury sprained ankle is when your ankle ligaments are overstretched, which results in soft tissue damage. The capsule that surrounds the ankle joint can also be damaged, causing bleeding within the tissues leading to a swollen ankle. Injuries can vary in their severity, from mild sprains through to severe ligament ruptures, and even broken bones. Ankle sprains can occur by simply rolling your ankle or some unstable ground. Some examples include awkwardly planting your foot when running, landing unevenly from a jump or stepping onto an irregular surface. Proprioception training is highly effective at helping to prevent ankle ligament injuries, as these exercises are designed to help players catch their balance when doing strenuous physical activities. Incorporating wobble boards and ankle braces can also help to improve the overall strength, stability and reflex of the ankle joint. You can also tape and brace your ankles during matches and training as this will help to reinforce the joint. The MCL is a ligament found in your knee that works in unison with other ligaments to give you stability when walking and running. An MCL injury is when the fibres that make up this ligament are torn or completely ruptured. There are roughly 3. An MCL injury is more likely to occur during sudden changes of direction or when the force of a tackle places excessive strain on the ligament causing a tear. This puts players who play in a back position at a higher risk of MCL injury due to their increased likelihood of being tackled and the need for fast changes of directions. To reduce the risk of an MCL injury, you should use effective conditioning training to improve the strength of your knee, as well as utilising speed work to improve the resilience of your knee to sudden changes of direction. A thigh haematoma is basically an extremely severe bruise as a result of damage to the blood vessels, which leads to blood leaking around the tissue resulting in the formation of a large clot. There are roughly 4. A haematoma occurs when there is a direct blow to the thigh area as a result of physical contact and impact. Given that rugby is a high contact sport, these types of injuries are part and parcel of the game. Unfortunately, in order to prevent this sort of injury, you would have to change what it is that makes rugby such a fantastic sport. Instead of focusing on prevention, it is better to focus on the introduction of a robust recovery plan as soon as possible after the injury occurs. Introducing RICE rest, ice, compression and elevation principles can help to significantly reduce recovery time and get you back to match fitness much sooner. Concussions are traumatic head injuries that occur from both mild and severe blows to the head. The RFU have created dedicated a web page with links to videos and downloadable guides to the exercise programmes, situated within the RFU RugbySafe web content. All RFU community rugby coaches have also been trained to deliver an Activate workshop to school and club coaches in England. From , free workshops were delivered across all regions in England with approximately coaches in total attending. Building on the success of the partnership between The University of Bath and the RFU, permission has now been granted for Activate to be used by World Rugby the World governing body for rugby union as its core injury prevention strategy for community rugby. In , Dr. As of July , Dr. Hislop has coordinated educator training programmes in 18 unions across Africa, North America, Oceania, Asia and Europe. The aim is for Activate to reach approximately 9. The online content has already been accessed by approximately different users from countries while a number of countries link directly to Activate on their rugby union governing body websites. University of Bath. Courses Research Enterprise Sport Departments About Staff Students Alumni. Open search. Back Courses Undergraduate courses Back Undergraduate courses Undergraduate virtual experience Graduate destinations Student stories Student blogs Postgraduate taught courses Back Postgraduate taught courses Postgraduate virtual experience Postgraduate virtual open days Practice Track Student stories Student blogs Postgraduate research courses Back Postgraduate research courses Doctoral College Doctoral research funding FindAPhD How to apply Student Services for doctoral students Experience Bath Back Experience Bath Webinars Living in Bath Virtual campus tour Open Days Student support. Back Placements Placements for students Back Placements for students Why choose a placement? Tap to Join! Click to Join! I understand that by providing my email address, I agree to receive emails from UPMC. I understand that I may opt out of receiving such communications at any time. Thank you for subscribing! You are already subscribed. Sorry, an error occurred. Please try again later. Get Healthy Tips Sent to Your Phone! Message and data rates may apply. Text the word STOP to opt out and HELP for help. Click here to view the privacy and terms. Connect with UPMC Find a Doctor. Patient Portal. |
| Reducing injuries in youth and adult rugby union | The first thing to think of is your first aid skills. ABCs - meaning Airway, breathing and circulation. If all these are fine, then have someone hold the player's head in a neutral position until he or she becomes conscious, and someone qualified comes to their aid. If the player is breathing, but still unconscious, the best thing to do is to leave them until this qualified person arrives. Once they are ready they need to gradually build in light rugby-specific skills and drills, extending themselves at training only as much as the injury allows. These tests should be a combination of those you used for the fitness tests at the start of the season and rugby skills and moves that the player will have to make during a game — like side stepping and tackling. You can use the Player Profiling information you recorded earlier in the year to see whether a player is ready to return to play based on a comparison of performance. Remember — if players continue playing with an injury they increase the chance of a further, more severe injury. Toggle navigation Rugby Toolbox. Search Login Sign up. Remember me. Forgot Password? Looking for something? Type your search below or try an advanced search. Combining: Combine the search features to narrow your search — e. Main Navigation Back Login Sign up. Rugby Toolbox RugbySmart Injury and concussion Injuries and Rehab. Concussion Injuries and Rehab Reporting a serious injury. Injuries and Rehab The general principles of caring for an injured player are: 1. Recognise when you need to do more, which may include calling an ambulance INJURIES Soft tissue injuries are the most common injuries in rugby for players. So, avoid Heat, Alcohol, Running and Massage. These will all make things worse. MOVING A PLAYER ON THE GROUND A player is knocked out cold. In this phase the player should be building up muscle strength around the injured area, working towards getting the full movement back in the joint, getting their balance back and keeping fit through activities like swimming and cycling. THE PLAYER NEEDS SUPPORT TO: Restore strength. Restore range of motion. Here are some of the best tips and tricks to prevent rugby injuries:. These are some of the most effective ways to prevent rugby injuries and they can easily be introduced into your routine. There is also an excellent Rugby Union Fact Sheet written by the Department of Planning and Community Development and VicHealth and published on the Sports Medicine Australia website. Click to read. Learn More. Read it here. The information provided on this blog is intended for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional advice or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this blog. Head injuries: Concussion Head injuries are a common injury that rugby players suffer, due to the amount of speed, contact and tackling that is done in rugby union. Overuse injuries Overuse injuries such as knee tendonitis or ankle tendonitis, stress syndrome involved with the media tibia, and bursitis are very common in rugby players. What is the most common injury in rugby union? What causes the most common injury in rugby union? How to Manage Rugby Injuries Rugby injuries are inevitable and being able to manage them is very important. Treatment of injuries caused by rugby To return to play the rugby player will have to work on strength, endurance, as well as flexibility. How to prevent rugby injuries Rugby has a high risk of injury. Here are some of the best tips and tricks to prevent rugby injuries: Wear protective gear. A mouthguard protects your teeth from being chipped or broken while a head guard cushions you against concussions. Use the correct technique. This is important as you must tackle and take a tackle in a way that your body absorbs all the force instead of breaking under it. Warm up and cool down. Stretching your muscles before you play helps prevent overuse injuries like tendonitis. Stay hydrated. Rugby expends a lot of energy and increases your blood temperature meaning you need plenty of water to stay hydrated. Rugby requires plenty of strength, endurance and even flexibility. Can Occupational Therapy Help My Dysgraphia Child? What Is Community Physiotherapy? Everything You Need To Know Read it here. Font Awesome Pro 6. Physio Inq National Support Offices. |

Wacker, Ihr Gedanke einfach ausgezeichnet